Apart from platelets and plasma, the human bloodstream also contains glucose that will be used as an energy source. Normally, the blood sugar will be controlled by insulin (a hormone produced in the pancreas). Thus, if the glucose level has excessively increased or decreased, it means that you may have diabetes and other health problems. This article will explain what level of blood sugar is considered dangerous as well as how to keep it under control.
What is a normal blood sugar level?
For healthy adults, the blood glucose level should be between 72 and 108 mg/dL, depending on each individual. However, it can be affected by stress, exercise, infections, age, and diet behavior. Besides, the sugar level can also go up and down during the day. For example, when you wake up with an empty stomach, the blood glucose will be a bit lower than usual, but after eating, it can rise up to 120-140 mg/dL.
In children, the blood sugar level is typically higher than in adults. For those aged lower than 6, the normal range is between 100-180 mg/dL while for children between 6-12 years old, it should be around 90-180 mg/dL.
What happens if the blood sugar level is too low?
In case your blood sugar level decreases lower than the target range or below 70 mg/dL, you may experience one or many of the symptoms below:
- Hunger
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Headache
- Confusion and difficulty in concentration
- Sweating
- Fainting
- Pale skin
- Rapid heart rate
If you have some symptoms above, and that you frequently feel dizzy, it could mean that you are facing the first signs of hypoglycemia (insufficiency of glucose in the bloodstream). In this case, you should see a doctor for a diagnosis.
What are the common diabetes symptoms?
When your glucose level is over 110 mg/dL on an empty stomach or more than 200 mg/dL, it means that you have an excess of glucose in the bloodstream which is called “hyperglycemia”.
Hyperglycemia can affect the arteries, heart, brain, and other organs, and may ultimately lead to diabetes. You may encounter the symptoms as follows:
- Hunger
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Thirstiness and dehydration
- Frequent urination
- Weight loss
- Skin irritation or infections
How can we track blood sugar levels?
In case you have diabetes, self-testing blood sugar is mandatory for you. For type 1 diabetes, you will need to test your blood 4-10 times a day while for type 2 diabetes, the frequency of blood sugar tests will vary to the amount of insulin you take. In order to check your blood glucose level, you can either use a blood sugar meter or a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). Let’s take a closer look at how these tools work:
Continuous glucose monitor (CGM):
A CGM is a small medical device used for continuous glucose level tracking. The best advantage of CGM is that it can send the result to your smartphone app in real-time and it will alert you if your sugar level is too low or too high.
To use this device, first, you have to clean the area where you will place the sensor. Then, insert a small sensor on your arm or abdomen. It will penetrate the top layer of your skin in order to track glucose levels through the fluid in your body. Remember that you need to change this sensor approximately every 2 weeks. Lastly, attach the transmitter to it and it’s done.
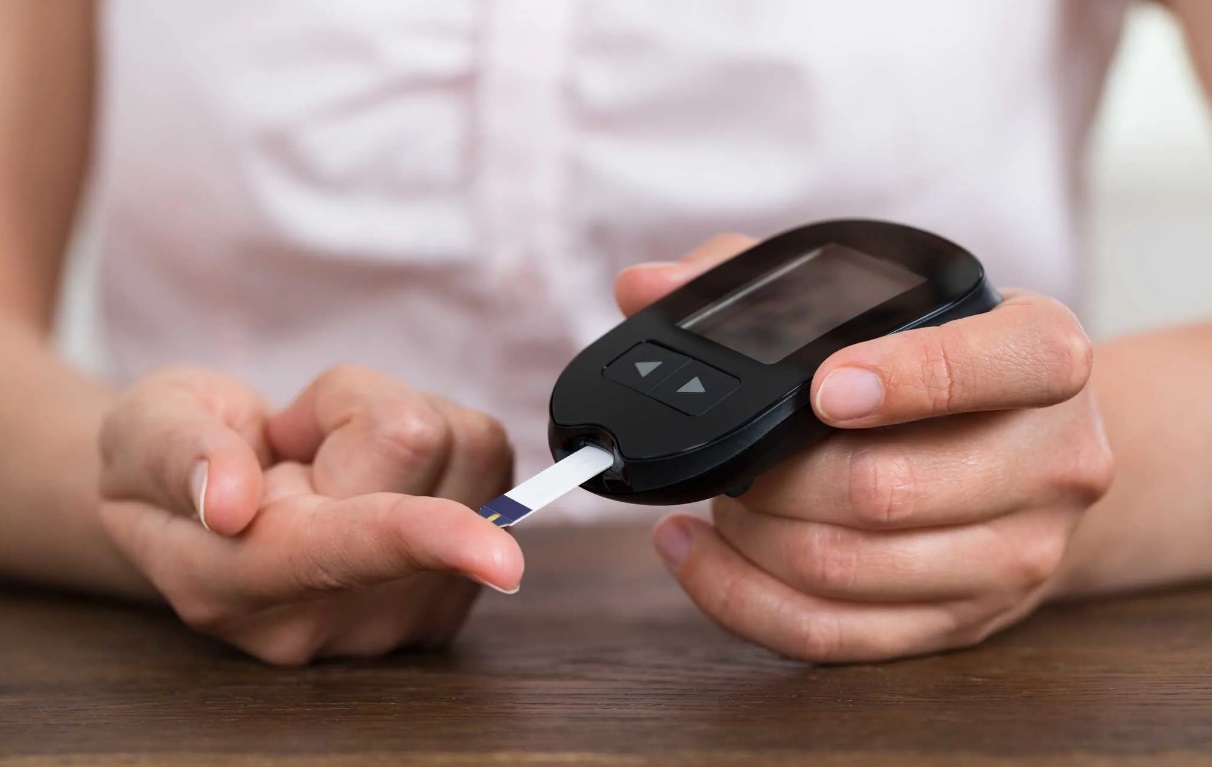
A blood sugar meter:
The latter is a portable electronic device that allows you to track blood sugar by yourself. Sometimes, your doctor may recommend using it along with a CGM in order to calibrate your CGM device. Below is how to properly use a blood sugar meter:
- Wash thoroughly your hands to rinse off all food stains and other remaining substances that may hinder the test result.
- Then, put a test strip into the device.
- After that, prick your fingertip with a lancing device or a needle in the test kit.
- Place your fingertip on a test strip and wait for the blood analysis result.
- A few minutes later, your blood sugar level will display on the meter’s screen.
Please note that the device’s instructions might be a bit different depending on the brand so you should always read carefully the manual beforehand.
If I’m diabetic, how to control my blood sugar level?
Although diabetes type 1 cannot be permanently cured, you can control your diabetes and decrease your sugar level naturally by following our instructions below:
- Change your diet behavior by consuming healthy diets, a lot of high-fiber vegetables, and low-sugar fruits like oranges, raspberries, avocados, etc. Furthermore, you must avoid high-carbs and sugary foods or drinks as well.
- Exercise regularly, at least 30 minutes daily because the glucose will be used for energy.
- Sleep sufficiently every night.
- Avoid stress.
Now, you know everything that’s important to know to prevent diabetes. Even if you don’t have diabetes, it is advised to reduce sugar and high-calorie food intake as well as to do daily workouts. Take care!